Experiment 1: To determine resistivity of two / three wires by plotting a graph for potential difference versus current.
Objective:
Required Apparatus :
Two resistance wires, a voltmeter (0-3)V and an ammeter (0-3 se) A of appropriate range, a battery/battery eliminator, a rheostat, a meter scale, a one-way key, connecting wires, and a screw gauge.
Theory / Formulae
According to Ohm’s Law:
$V \propto I \Rightarrow V = IR \Rightarrow R = \frac{V}{I}$
Resistivity \rho is given by:
$\rho = \frac{R \cdot A}{L}$
where:
- R: resistance from V-I graph
- $A = \pi r^2 = \frac{\pi d^2}{4}$ : cross-sectional area
- L : length of the wire
Circuit Diagram :
Observations:
- Range of ammeter = (0 – 3) A
- The least count of ammeter = 0.05 A
- Range of voltmeter = (0 -3) V
- The least count of voltmeter = 0.05 V
- The least count of metre-scale (L.C.) =0.1 cm
L.C. of the given screw gauge:-
Pitch of screw gauge = 1 mm
Total number of divisions on the circular scale = 100
L.C. of the given screw gauge = Pitch / No. of divisions on the circular scale
= 0.01 mm = 0.001 cm
For 1st wire:
Length of the given wire, L= 15 cm = 0.15 m
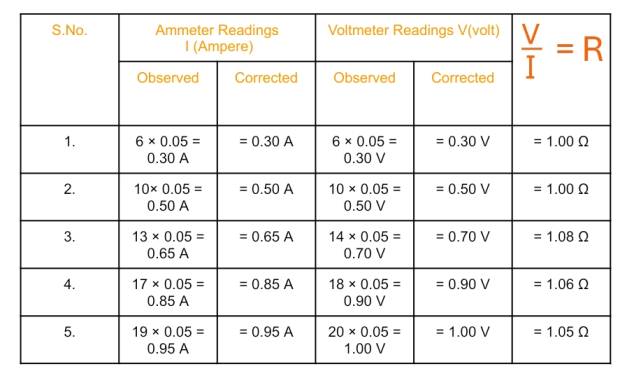
Observation Table for Resistance :
Mean value of resistance, R= 1+1+1.08+1.06+1.05/5 = 1.04 ohm
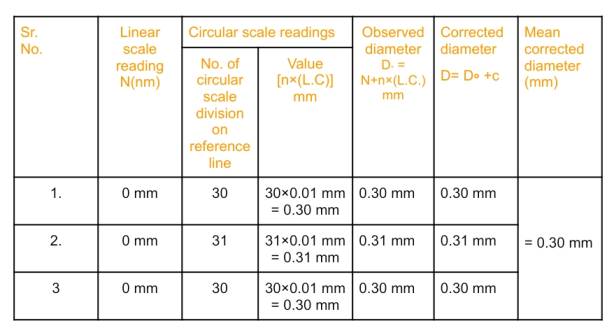
Table for Diameter of wire:
Calculation for Specific Resistance:
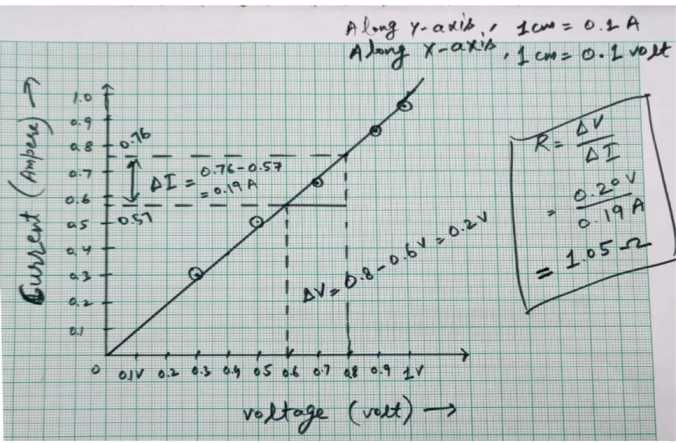
Graph – Potential difference versus Current
For 2nd wire:
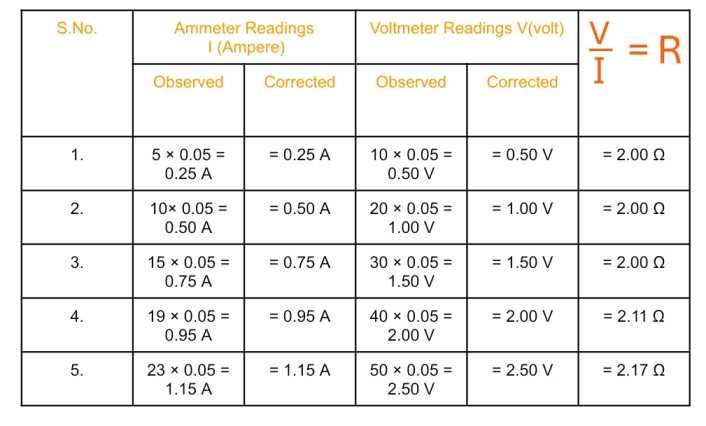
Observation table for Resistance:
Table for Diameter of wire:
Calculation for Specific Resistance:
$\rho = \frac{R\pi D^2}{4L} = \frac{2.06 \times 3.14 \times (3 \times 10^{-4})^2}{4 \times 0.29} \text{ ohm-m}$
$\rho= 50.19 \times 10^{-8} \text{ } \Omega\text{-m}$
Standard value of the specific resistance of the material (Constantan) of the given wire
$\rho_0 = 49 \times 10^{-8} \text{ } \Omega\text{-m}$
Percentage error =$ \frac{\rho - \rho_0}{\rho_0} \times 100 \% = \frac{(50.19 - 49) \times 10^{-8}}{49 \times 10^{-8}} \%$
Percentage error = 2.43 %
Graph – Potential difference versus Current:
Result :
- Resistance of first wire from table = $1.04 \Omega$ and from graph $1.05\ \Omega$
- Resistivity of 1st wire = $48.98 \times 10^{-8}\ \Omega\text{-m}$
- Percentage error = 0.04%
- Resistance of 2nd wire from table = $2.06 \Omega$ and from graph = $2.00\ \Omega$
- Resistivity of 2nd wire = $50.19 \times 10^{-8}\ \Omega\text{-m}$
- Percentage error = 2.43%
Precautions:
- The connection should be neat, clean, and tight.
- Thick connection wires should be used for the connections.
- The voltmeter and ammeter should be of proper range.
- A low-resistance rheostat should be used.
- The key should be inserted only while taking observation to avoid heating of resistance.
- At one place, the diameter of the wire should be measured in two mutually perpendicular directions.
- The wire should not make a loop.
Source of Error:
- The instrument connections may be loose.
- Thick connection wires may not be available.
- Rheostat may have high resistance.
- The wire may not have uniform thickness.
- The screw gauge may have faults like a 'backlash' error and a wrong pitch.